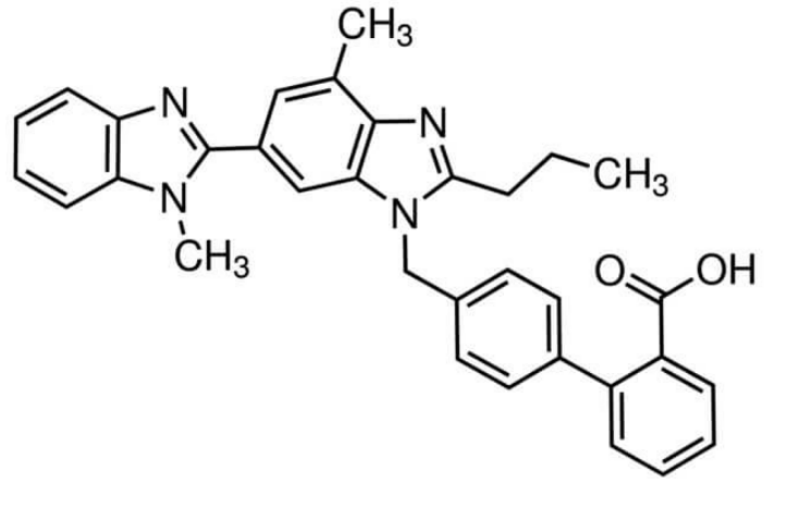
Cas number: 54-31-9 Molecular Formula:C12H11ClN2O5S
| Melting Point | 261-263°C |
| Density | 1.16 (rough estimate) |
| storage temp | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: >5 mg/mL at 60 °C |
| optical activity | N/A |
| Appearance | Off-White Solid |
| Purity | ≥98% |
Telmisartan was launched in the US for the treatment of hypertension. It can be prepared in eight steps starting with methyl 4-amino-3-methyl benzoate; the first and second cyclization into a benzimidazole ring occur at steps 4 and 6 respectively. Telmisartan blocks the action of angiotensin II (Ang II), the primary effector molecule of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). It is the sixth of this class of 《sartans》 to be marketed after the lead compound Losartan. Its long lasting effect (24h half-life) could be the main difference with other angiotensin II antagonists. Unlike several other agents in this category, its activity does not depend upon transformation into an active metabolite, the 1-O-acylglucuronide being the principal metabolite found in humans. Telmisartan is a potent competitive antagonist of AT1 receptors that mediate most of the important effects of angiotensin II while lacking affinity for the AT2 subtypes or other receptors involved in cardiovascular regulation. In several clinical studies, Telmisartan, at a once daily dosage, produced effective and sustained blood-pressure lowering effects with a low incidence of side effects (particularly treatment-related cough associated with ACE inhibitors in elderly patients).
Telmisartan is an angiotensin II receptor antagonist.