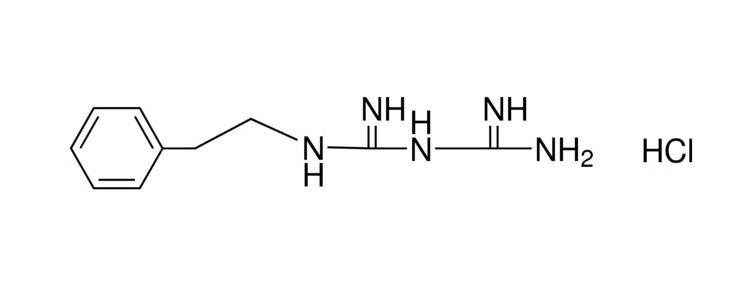
Phenformin Cas number: 834-28-6 Molecular Formula: C10H16N8
| Melting Point | 150-155℃ |
| Density | 1.197g/cm³ |
| storage temp | 2-8℃ |
| solubility | It has a certain solubility in water, is easily soluble in methanol and isopropanol, and is difficult to dissolve in chloroform and ether |
| optical activity | +27.0 degrees (C=1, water). |
| Appearance | white crystalline powder |
Phenformin is mostly used to treat adult non insulin dependent diabetes and some insulin dependent diabetes. The function is to promote the uptake and glycolysis of glucose by muscle cells, reduce the production of glucose by the liver, and have an anti hyperglycemic effect. It can be used in combination with insulin, making it easier to control blood sugar and reducing insulin dosage. For obese diabetes, it can also be used to inhibit appetite and absorb glucose in the intestine to reduce weight.
Phenformin is mostly used to treat adult non insulin dependent diabetes and some insulin dependent diabetes. The function is to promote the uptake and glycolysis of glucose by muscle cells, reduce the production of glucose by the liver, and have an anti hyperglycemic effect. It can be used in combination with insulin, making it easier to control blood sugar and reducing insulin dosage. For obese diabetes, it can also be used to inhibit appetite and absorb glucose in the intestine to reduce weight.
Oral administration: The commonly used dosage is 50-200mg per day, taken in three doses. Initially, take 25mg once, 2-3 times a day, before meals. It can gradually increase to 50-100mg per day. Generally, blood sugar decreases after one week of medication, but in order to reach normal blood sugar levels, medication needs to continue for 3-4 weeks.